This article deals with the Amendments in the Intended Use of Medical Devices in the field of Physical Support. The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) is the Indian Advisory Body for Pharmaceuticals and Medical Device Regulations in India wherein all Notified Medical Products are regulated by them. The responsibility lies with the Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) under the CDSCO for product approvals in India. The CDSCO manages approval and regulation Drugs, Cosmetics, IVD’s and Medical Devices, control over the quality of Imported Devices, coordination of the activities of State Drug Control Organizations and providing expert advice with a view of bringing about uniformity in the enforcement of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act. Manufacturers can leverage their approvals in the US, Canada, Europe, Australia or Japan for the Registration Process in India. The Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 is an act of the Indian Parliament which is responsible for the Medical Device Regulations in India & regulation of Importation, Manufacturing and Distribution of Drugs, Cosmetics, Medical Devices and IVD’s in India. The most important objective of this Act is to enforce that quality standards are adhered to and every device imported into India is protected. This article focuses on the Medical Device Regulations in India. To know more on the regulatory pathway – Click Here
Medical Device Regulations – Amendment on Intended Use of Products Used in Physical Support
With several changes being constantly introduced by the CDSCO, this current change is mainly dealing with the Intended Use of Various Products. The CDSCO has classified Appendix A based on the Intended Use, Risks Associated and Other Parameters Specified with the device. The General intended Use has been given by the CDSCO, however, Specific Intended Use can be given by the manufacturer. This list is dynamic and is subject to changes. The following is the table which has been published by the CDSCO for products dealing with Medical Devices in Physical Support along with their Intended Use.
Table –
| S.No. | Medical Device Name | Intended Use | Risk Class |
| 1 | Ankle continuous passive motion exerciser | Electrical devices intended to continuously move the ankle joint (e.g., flexion, inversion/eversion) without patient assistance during continuous passive motion (CPM) exercise therapy usually following surgery or trauma to the joint. | B |
| 2 | Ankle/foot orthosis | Intended to encompass the ankle joint, or the ankle and foot, to support, align, prevent, or correct orthopaedic deformities/injuries or to improve function of the ankle and/or foot; it may also be intended to offload and redistribute foot pressures that affect pedal circulation to improve blood flow and help heal diabetic foot ulcers or post surgical wounds. | A |
| 3 | Balance board | Intended to train patients with difficulties in balance (e.g., a paraplegic or a stroke victim) walks for balance training. | A |
| 4 | Bed traction frame | Intended to treat patients with fractures and other orthopaedic disorders (e.g., of the lower or cervical spine, hip). | A |
| 5 | Body arch traction table | Intended to support the body of a patient and provide traction for the back muscles and spine by flexing the patient into a reverse supine body arch. | A |
| 6 | Canalith repositioning procedure chair, manual | Intended to treat balance disorders [e.g., benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), canalithiasis] caused by displaced canaliths (otoconia) in the inner ear of the patient | A |
| 7 | Cervical spine collar | Intended to support or immobilize the cervical spine to treat deformities, fractures, sprains, or strains (often to treat whiplash resulting from an automobile accident). | A |
| 8 | Cervical spine immobilization head ring | Intended to be fixed to the skull of a patient at brow level using pointed, steel, threaded bolts (typically four) that are adjusted to penetrate the outer bone of the skull. | D |
| 9 | Cervicothoracic spine orthosis | Intended to support or immobilize deformities, fractures, sprains, or strains of the cervicothoracic spine. | A |
| 10 | Cervical Thoracolumbosacral spine orthosis | Intended to encompass the cervical thoracolumbosacral spine region of the neck and trunk. | A |
| 11 | Chest-oscillation airway secretion clearing system | Intended to rapidly inflate and deflate against the chest wall of the patient for promoting airway clearance by creating high frequency chest wall oscillation (HFCWO), resulting in the mobilization of bronchial secretions. | B |
| 12 | Collar and cuff arm sling material | Fabric and form composite material intended to immobilize forearm, elbow, humerus or shoulder injuries. | A |
| 13 | Cranial orthosis | Intended to be worn on the head of an infant with an abnormal head shape (e.g., due to plagiocephaly, brachycephaly, scaphocephaly), or after craniosynostosis repair surgery, to apply pressure to the cranium and improve cranial symmetry/shape during growth over a period of months. | A |
| 14 | Elbow orthosis | Intended to encompass the elbow joint to support, align, prevent, or correct deformities/injuries or to improve function of the elbow. | A |
| 15 | Finger orthosis | Intended to encompass the whole or part of the finger to support, align, prevent, or correct deformities/injuries or to improve function of the finger. | B |
| 16 | Flotation therapy bed, adult | Intended to minimize pressure points on a patient’s body by providing contact with as much of the body surface as possible, typically through a mattress that contains a large volume of constantly moving media, e.g., water, air, or mud that lifts the patient to simulate a floating effect. | B |
| 17 | Flotation therapy bed, neonatal | Intended to minimize pressure points on neonatal patient’s bodies by providing contact with as much of the body surface as possible, typically through a mattress that contains a large volume of constantly moving media, e.g., water, air, or mud that lifts the patient to simulate a floating effect. | B |
| 18 | Foot orthosis | Intended to encompass the whole or part of the foot, or designed as a plantar insert, and intended to provide rigid or semi-rigid correction of the foot for persons with orthopaedic deformities/injuries of the feet | A |
| 19 | Hand orthosis | Intended to encompass the whole or part of the hand to support, align, prevent, or correct deformities/injuries or to improve function of the hand. | A |
| 20 | Hand/finger splint | Intended to immobilize an injured hand to protect injuries to, e.g., the digits, metacarpals, and wrist during the healing process. | A |
| 21 | Hand/wrist continuous passive motion exerciser | Hand/wrist continuous passive motion exerciser | B |
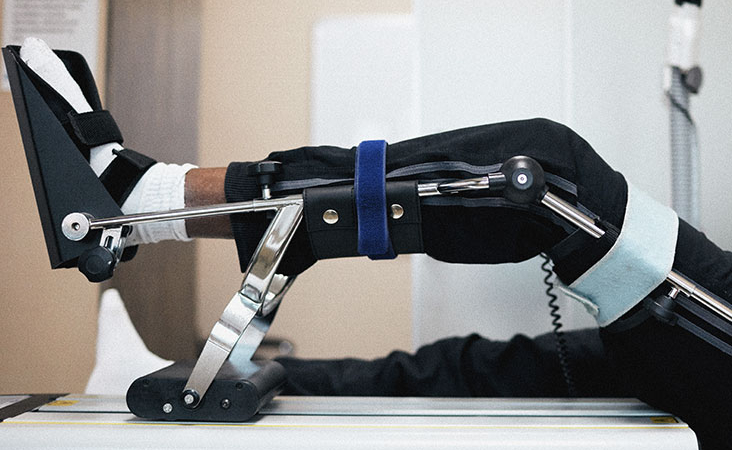
| 22 | Hip/knee continuous passive motion exerciser | A mains electricity (AC-powered) device Intended to provide continuous passive motion (CPM) exercise therapy for the hip and/or knee, typically following joint surgery/trauma to promote healing; some types may also operate with patient assistance under controlled active motion (CAM). | B |
| 23 | Horizontal non-powered traction system | Non powered device intended to be attached to a table for the application of constant horizontal traction forces to the cervical or lumbar vertebrae by means of attached harnesses whilst the patient typically lies in a supine position on the table during treatment. | A |
| 24 | Incentive spirometer | Intended to be used in respiratory therapy to encourage and motivate deep-breathing manoeuvres, typically for the postsurgical treatment and prevention of atelectasis (lung collapse) and to help facilitate airway opening and clearing. | A |
| 25 | Intermittent traction system | It is an AC powered electronic device. Intended to apply and relieve pre-set traction forces from a motor through harnesses typically attached to the cervical or lumbar vertebrae. | B |
| 26 | Kinetic bed | Intended to enable continuous change of the patient’s lying position, e.g., it can tilt the entire bed mattress support system (this includes the mattress, the framework that supports the mattress,and the bedding) lengthways, sideways or to a near vertical tilt. | A |
| 27 | Knee immobilizer | Intended to temporarily render the knee immovable, either preoperatively or following injury or arthroscopy. | A |
| 28 | Neuro-controlled ambulation exoskeleton | Intended to assist a patient with a walking disability (neurogenic, muscular, or osseous in origin) regain lost motor function by transmission of the patient’s residual nerve function, via cutaneous electrodes, to the device motor assembly. | C |
| 29 | Orthopaedic bed | Intended to provide support for skeletal traction to stabilize fracture sites. | A |
| 30 | Paediatric dorsiflexion slant board | Intended to be used in the treatment of various medical conditions (e.g., congenital, neurological, post- traumatic) in paediatrics, where tendon tightness and muscle contracture affect the ability to dorsiflex the foot, possibly leading to an abnormal gait | A |
| 31 | Parapodium walking frame | Intended to encompass and provide support for the body of a patient who is unable to stand unassisted to help them move (walk) by changing their centre of gravity (COG). | A |
| 32 | Physical therapy massager | Electrically powered device intended to provide therapeutic massage to a larger area than hand-held massaging devices. | B |
| 33 | Shoulder continuous passive motion exerciser | It is a mains electricity (AC-powered) device Intended to continuously move the shoulder joint (e.g., flexion, rotation, adduction/abduction) without patient assistance during continuous passive motion (CPM) exercise therapy usually following surgery or trauma to the joint. | B |
| 34 | Shoulder immobilizer | Intended to temporarily immobilize or limit abduction of the shoulder joint to support healing of an injury or a surgical wound. | A |
| 35 | Swivel-walker | Intended to encompasses and provide support for the body of a patient who is unable to stand unassisted, to help them move (walk) by rocking sideways (shifting their weight from side-to-side with a shoulder movement) which makes the footplate of the device swivel so that it “walks” forward. | A |
| 36 | Toe separator | Intended to space the toes of the foot to relieve pain, pressure/friction between toes, and/or to facilitate realignment of the toes to a natural position. | A |
| 37 | Traction table, line- powered | Intended to support a patient and to provide traction for the back muscles and spine (e.g., lumbar, cervical) by a motorized mechanical manipulation of the spine. | B |
| 38 | Wrist immobilizer | Intended to temporarily render the wrist immovable as therapy for non- displaced fractures, strains, sprains, and muscle injuries of the wrist. | A |
Conclusion
To obtain Regulatory Consultancy, contact Morulaa. We at Morulaa can help you learn more about your Medical Device Regulations. Subscribe to our Website for Regulatory Consultancy wherein you learn about the Latest Rules and Medical Device Regulation.

Leave a reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.